
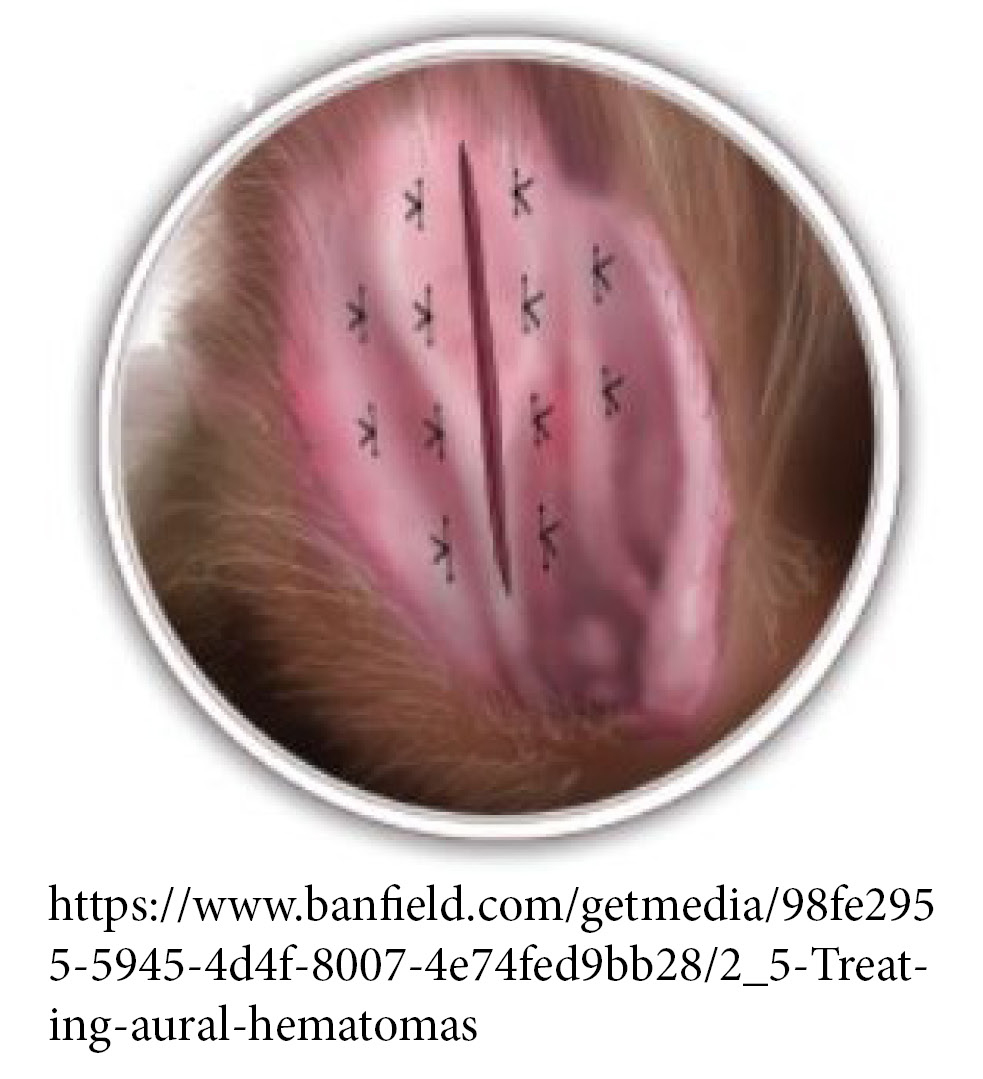
There’s always the chance that a small hematoma might not need to be treated they can resolve on their own as the blood becomes reabsorbed. Additional allergy testing may need to be conducted.Īn ear hematoma is painful for a dog, so it’s important to have it examined as soon as possible.
AURAL HEMATOMA SURGERY TRIAL
This can be a bit trickier than simply examining samples under a microscope some trial and error may be required to identify the allergen. This exam will include taking a swab from the ear canal and looking under a microscope for bacteria and yeast (which is referred to as cytology).įood trials/skin tests to identify food or other allergies that can cause discomfort. Needle aspiration, which will confirm that the fluid in the pocket is blood.Įxamination of the ear canal to check for signs of infection, parasites, and/or foreign bodies lodged in the ear canal. The initial evaluation may include, but is not limited to, the following tests: So the next step after a physical exam is to focus on the reason behind the head-shaking and/or scratching. What’s more important when determining treatment is understanding what caused the hematoma in the first place. The hematoma itself is easily identifiable and not difficult for a veterinarian to diagnose by visual examination. The vast majority of aural hematomas are caused by infection or allergies.

Yeast infection or another type of bacterial infection
AURAL HEMATOMA SURGERY SKIN
The space between the ear cartilage and skin fills up with blood and fluid, causing the ear to swell rather quickly, and forming a balloon-like nodule on the dog’s ear.Īny breed of dog can develop ear hematomas, but those with larger ear flaps are more susceptible, because the ear flaps slap against the skull when the head is shaking.īut what triggered the head-shaking and scratching, which in turn caused the hematoma to form? There are a number of underlying conditions that could be the culprit: The tissue of the ear flap (or “pinna”) is very thin, and when it’s injured, the blood vessels can break. An ear hematoma in dogs can be caused by aggressive head-shaking and/or scratching.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
